WHAT ARE SUBMETERS AND WHY USE THEM?
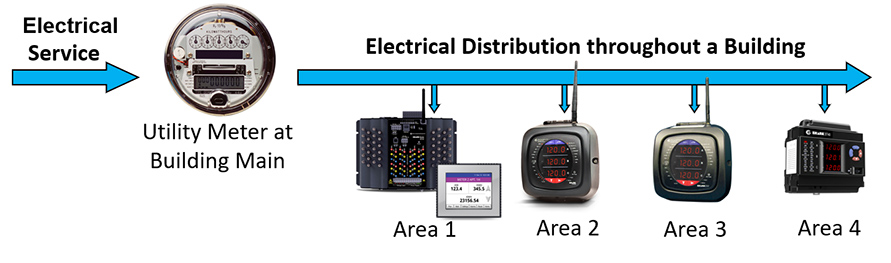
Submeters Monitor Specific Areas within a Building
- Submeters are meters used to determine the amount of energy used
within specific areas of a building. - The energy measurements are then used to allocate or bill for
electrical usage by tenants or departments within the building.

Benefits of Submetering?
- Submetering Saves Energy. Submetering buildings produces an annual savings of up to 18-30% of total electrical consumption in the first year.
- Submetering Energy Savings Persist Over Time. Submetering savings are maintainable over long periods of time because:
(a) Conservation is reinforced by the resident’s receipt of an electric bill.
(b) Residents will invest in efficiency (e.g., more efficient refrigerators and lighting) because they will reap the benefits directly. - Approximately 60-70% of Tenants Benefit from Submetering. The only tenants who fare worse under Submetering than under other means of allocating electric cost are those who use excessive amounts of electricity.
- Submetering is Fair. Submetering simply restores the “user pay” concept. Tenants pay for what they use and will change their habits to improve efficiency.
- Submetering Benefits Owners. Submetering largely eliminates variable and difficult-to-control factors from a building’s operating budget. Owners can better predict costs when the only energy usage to be considered is for common areas under management control.
Shark®100S Submeter
Multifunction WiFi Electric Submeter
Key Features:
- ANSI C12.20 0.2 Accuracy Class energy measurements.
- Standard RS485 Communication; Modbus RTU/ASCII and DNP3.
- Simultaneous Ethernet and WiFi communication; Modbus TCP.
- Bright red LED display with three .56″ lines.
- Built-in KYZ pulse for accuracy testing.
- Limit alarms and THD.
- Standard IrDA for meter configuration.


Shark® 200S Submeter
Data Logging WiFi Electric Submeter
Key Features:
All of Shark® 100S meter features*, plus:
- Load profiling and trending, including:
- Three historical trending logs of 64 parameters each.
- Limits/alarm log.
- System Events anti-tampering log.
- Advanced metering: Transformer Line Loss and CT/PT compensation.
(*THD not available.)
Shark® MP200
Data Logging Multipoint WiFi Energy Meter
Key Features:
- ANSI C12.20 0.2 Accuracy Class energy measurements.
- Rugged, space saving design consolidates multiple metering
points into one processing CPU. - 24 single or 8 three phase circuit metering.
- Two historical trending logs – over eight years of logging.
- Standard RS485 Communication; Modbus RTU/ASCII.
- Simultaneous Ethernet and WiFi communication; Modbus TCP.
- Transducer and remote LCD color touchscreen display for easy retrofit installation in a panel.
- Front USB port for direct data download and meter configuration.
- Built-in KYZ pulse for accuracy testing.
- Limit and control capability.
- Standard CTs; can ignore reverse CTs for easier
installation. - Stud inputs for substation and critical infrastructure.
- Optional pre-wired NEMA 1X enclosure.



ST40 Meter
Compact DIN Rail Electric Submeter with Power Quality
Key Features:
- Small footprint for machine level monitoring, solar, wind, and other
applications with limited installation space. - ANSI C12.20 0.2 Accuracy Class energy measurements.
- Power quality waveform recording at up to 512 samples per cycle.
- Extensive memory for logging load profiles, system events,
limits, and alarms. - Modbus, BACnet/IP, or DNP3 for software integration.
- RJ45 Ethernet or RS485 com ports.
- Advanced metering features: Transformer line loss and CT/PT compensation.